timeaggs
Description
Performs search and generates an array of data distributed along a timeline using the internal mechanisms of the storage system.
The timeaggs command can only be used in a query if it's preceded by other commands that also work with internal storage mechanisms, such as source, search, and peval. This condition must also be met for all subqueries within the query.
Syntax
timeaggs [<composite>] [<span>] [<timefield>] [<limit>] [<useother>] <functions-expression> ["," <functions-expression>] [<by_expression>]
Required Arguments
functions-expression You must use at least one of the following functions:
| Parameter | Syntax | Description |
|---|---|---|
count | count | count(<field>) | Counts the number of events containing a field. If no field is specified, counts the total number of events. |
avg | avg(<field>) | Calculates the average value of a given field. |
dc | dc(<field>) | Computes the number of unique values in a given field. |
max | max(<field>) | Computes the maximum value in a given field. |
min | min(<field>) | Computes the minimum value in a given field. |
sum | sum(<field>) | Computes the sum of the values in a given field. |
Optional Arguments
| Parameter | Syntax | Default | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
span | span=<span> | see predefined span values | Defines the interval for distribution of segments. |
timefield | timefield=<field> | @timestamp | Name of the field containing the timestamp. |
composite | composite=<boolean> | false | Allows for scrolling in aggregations and obtaining all possible segments (buckets) through multiple queries (similar to scroll in stats). Can only be applied when grouping (by fields). The number of segments (buckets) returned in the response is fixed at 1000. |
limit | limit=<int> | 10 | The maximum number of unique by_field values that can be used in the column names of the result. Remaining values will be merged into the OTHER field. |
useother | useother=<boolean> | true | If set to false, the limit parameter is ignored. |
by_expression | by <field> | The field name used for grouping values. |
The following time formats are allowed: (+|-)<int>(s|m|h|d|w|month):
- s/sec/secs/second/seconds - seconds
- m/min/mins/minute/minutes - minutes
- h/hr/hrs/hour/hours - hours
- d/day/days - days
- w/week/weeks - weeks
- mon/month/months - months
span valuesIf no span parameter is specified for the time field, default parameters will apply.
Here's the list of predefined parameters:
| Time Interval | span |
|---|---|
| last 15 minutes | 10 seconds |
| last 60 minutes | 1 minute |
| last 4 hours | 5 minutes |
| last 24 hours | 30 minutes |
| last 7 days | 1 day |
| last 30 days | 1 day |
| last year | 1 month |
compositeThe composite argument is available when querying OpenSearch.
keyword in OpenSearchAggregations in OpenSearch perform statistical operations on numeric fields or text fields of the keyword type. Thus, for text fields, you need to append <fieldname>.keyword, and this is necessary both in specified fields and by fields. For example:
... | timeaggs avg(user.keyword), earliest(country.keyword) by event.keyword, user_count
Query Examples
Example 1
Calculating the average number of messages per user by hourly intervals:
... | timeaggs span=1h avg(msgNums) by user.keyword
In this example, for each unique value of the user.keyword field, the average number of messages msgNums is calculated for each hourly interval.
Example 2
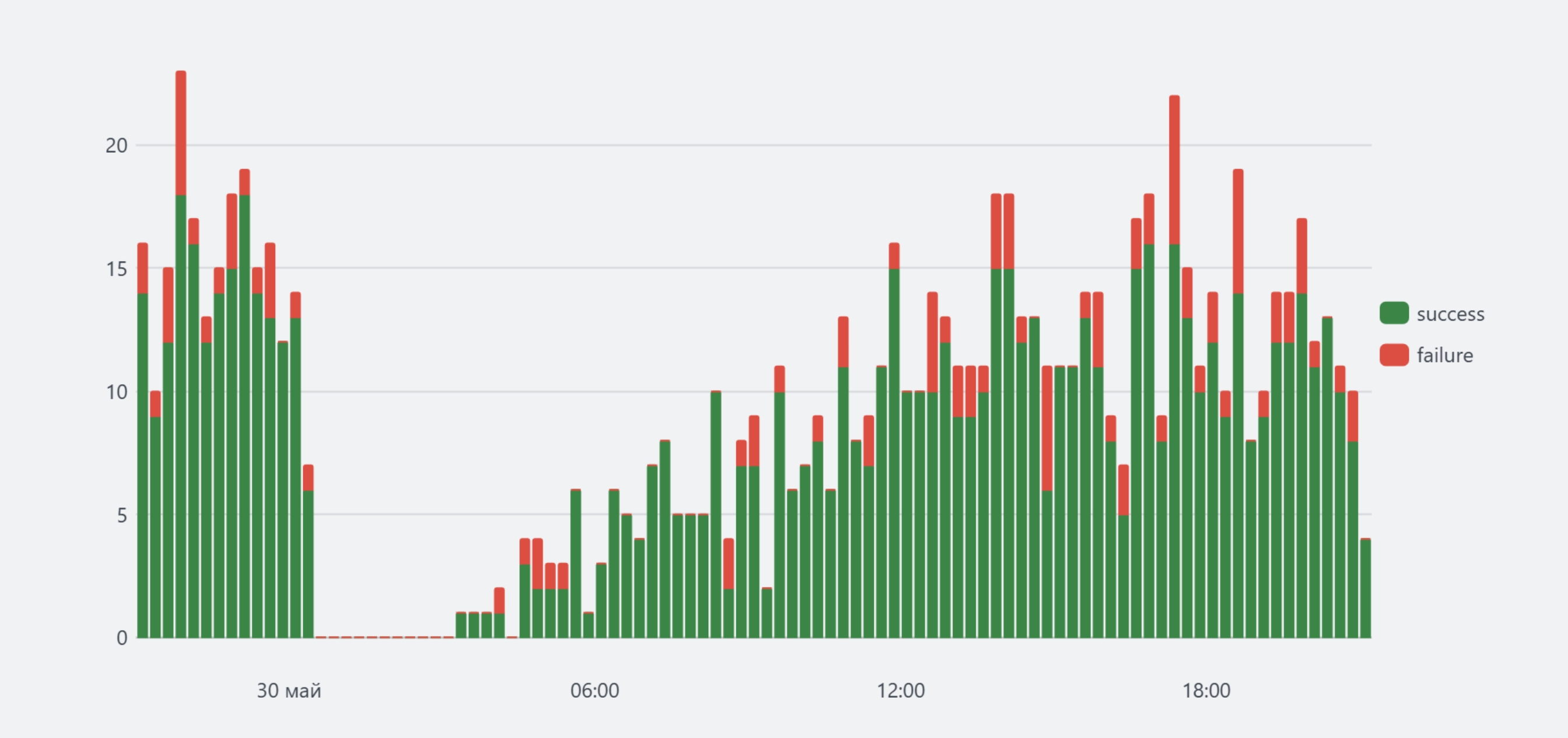
In this example, for each unique value of the event.outcome field, data is aggregated over a 15-minute time interval with a count of events.
... | timeaggs span=15m count by event.outcome
For the sample input data presented below, a bar chart with series grouping is built:
| username | request | path | status | event.outcome |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Smith | GET | /veil | 200 | success |
| Taylor | GET | /cherry | 200 | success |
| Smith | POST | /fuel | 403 | failure |
| John | GET | /quilt | 200 | success |
Example 3
Calculating the total number of events and the maximum log offset by 3-hour intervals:
... | timeaggs composite=true span=3h count, max(log.offset)
Example 4
In this example, for each 5-day interval, the system will return the value of the log.offset field that occurs in 5 percent of cases:
... | timeaggs span=5d perc(log.offset, 5)
Example 5
Calculating the maximum network traffic volume for each host by 30-minute intervals with a limit on the number of unique hosts:
In this example, a new field network.kb is created, which converts the values of the network.bytes field to kilobytes; the round command rounds the kilobytes to 2 significant digits and saves them to a new field network.kb_round.
... | peval network.kb=network.bytes/1024, network.kb_round=round(network.kb, 2)
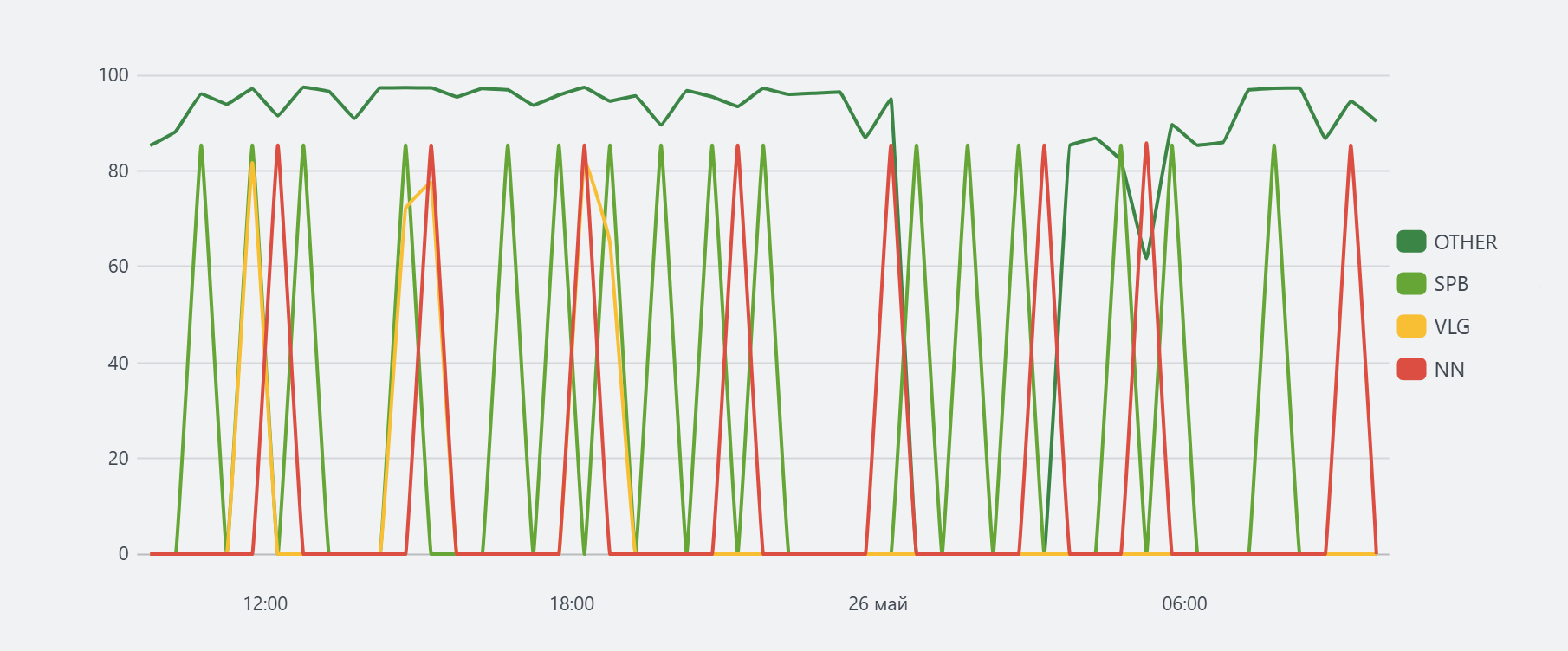
| timeaggs limit=3 span=30m max(network.kb_round) by hostname
For each unique host value hostname, the maximum network traffic volume network.kb_round is calculated for 30-minute intervals. The limit=3 parameter limits the number of unique hosts in the result to three; the remaining hosts are combined into the OTHER column.
| timeaggs limit=3 span=30m max(network.kb_round) by hostname
Sample input data:
| hostname | network.bytes | @timestamp |
|---|---|---|
| SIN | 72343 | 2025-05-26T15:25:39.697685Z |
| BJS | 85804 | 2025-05-26T15:25:33.003472Z |
| NN | 60239 | 2025-05-26T15:25:24.338701Z |
| SIN | 10646 | 2025-05-26T15:25:24.290198Z |
| BJS | 10646 | 2025-05-26T15:25:25.223198Z |
The query execution result may be the following table:
| OTHER | SIN | BJS | NN | _time |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 99,84 | null | null | 87,4 | 2025-05-26T16:00:00.000Z |
| 91,71 | 87,409 | null | null | 2025-05-26T16:30:00.000Z |
| 85.36 | null | 89,75 | 15,96 | 2025-05-26T16:30:00.000Z |