Working with Time Filters
General Description
On the search page, as well as on most Search Anywhere Framework dashboards, there is a time filter designed to select a time interval for which information will be displayed.
Time filtering is one of the main tools for managing the data range. By choosing the appropriate time interval, you can significantly reduce the use of system resources and improve the efficiency of data search and analysis.
Using Time Filters
Choosing the right time range allows narrowing down the search to the most current and relevant data. For example, if you are interested in analyzing only the last 24 hours, filtering by this time interval will exclude outdated data, which in turn will reduce the volume of processed data and improve system performance.
Moreover, proper time filtering helps to avoid unnecessary consumption of system resources on processing unnecessary information. This is especially important when working with large volumes of data, as complex queries may slow down system performance.
Search Anywhere Framework offers several options for time filters to provide convenient data filtering:
- Relative time intervals
- Absolute time intervals
- Real-time data updates
For more information on how to use time intervals, you can read the Time Ranges section.
Brief Information on Types of Time Intervals
Relative Time Intervals
By default, the time interval value is set to 24 hours ago - displaying statistics for the last 24 hours. To select a different time interval, simply click on the calendar icon on the left side of the filter and choose the desired value.
Absolute Time Intervals
Absolute time intervals allow users to set exact start and end dates and times for the interval for data analysis. This allows for more precise query tuning and obtaining information only for a specific period of time that interests the user.
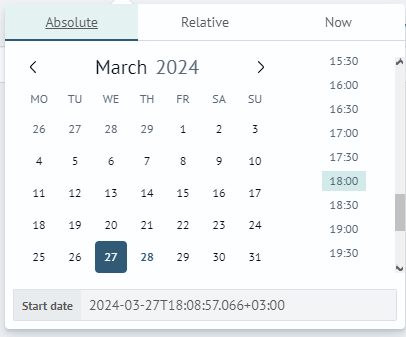
Real-time Data Updates
Real-time data updates are a feature that automatically refreshes the information on the screen to the current moment in time. This allows users to receive the freshest information without manually refreshing the page or requesting new data.
When the user selects the current time interval, the system automatically updates the data every time there is a change in the data source. For example, if website traffic data is being analyzed, the source may be constantly updated with new visit data, and the information on the screen will be updated accordingly.