Management SAF Beat
Overview
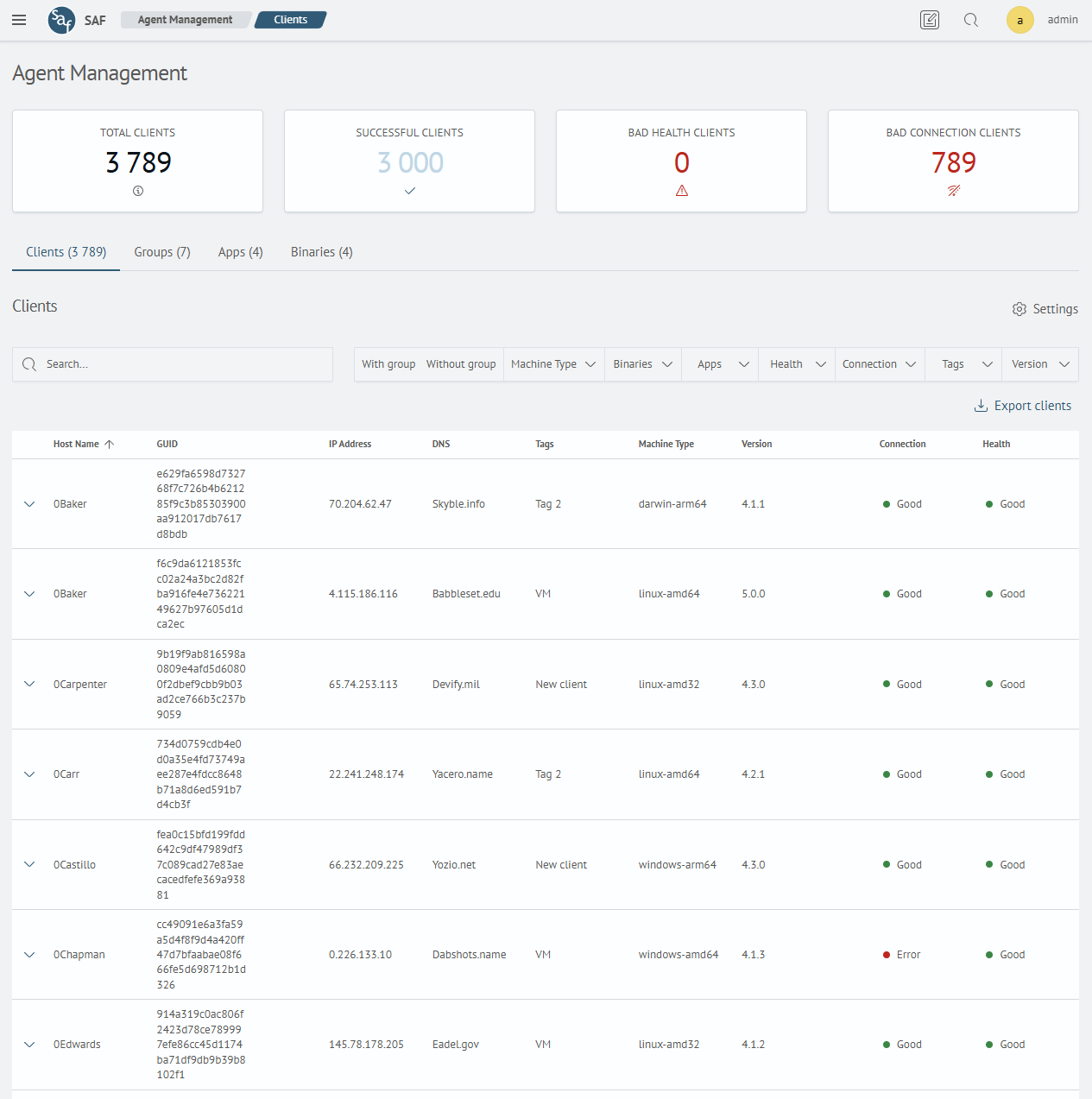
This interface is designed for configuring agent-based data collection using SAF Beat, as well as for analyzing client data. The interface provides the following functionality:
- Viewing client statistics
- Viewing client data collected by the SAF Beat agent, with data filtering options
- Exporting client data as a JSON or CSV file
- Viewing and editing client groups
- Viewing and editing application configurations
- Viewing and editing files
The appearance of the interface is shown in the image below: