Replicas in Search Anywhere Framework
What are Replicas?
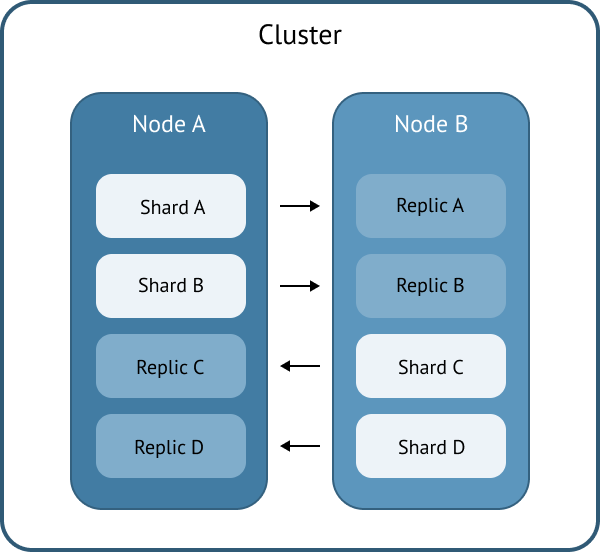
In data storage systems, there are two types of data (shards): primary and replicas. The system stores one or more copies of the data to ensure fault tolerance and improve performance.
Advantages
-
Fault Tolerance. Replicas ensure high availability and fault tolerance. In case of a node failure, data can be retrieved from a copy (replica) on another node, avoiding data loss. Additionally, replicas allows for continued indexing of new data.
-
Improved Search Performance. Distributing data across replicas allows queries to be distributed among different nodes. This increases the system's throughput and reduces latency in query execution. For environments with a high volume of concurrent queries, we recommend having at least one replica.
-
Fast Recovery from Failures. In case of a temporary failure or node outage, replicas allow for quick recovery of system functionality. Since the data is already on the replicas, there is no need to fully restore it from other nodes.
-
Maintenance Without Downtime. With replicas, system maintenance and updates can be performed without downtime. Some nodes can be taken offline for maintenance while others continue to handle queries and indexing, thanks to the presence of replicas.
Disadvantages
-
Additional Resource Costs. Using replicas requires additional resources, such as disk space and processor time.
-
Potential Impact on Indexing Speed. An excessive number of replicas can impact the speed of data indexing.